Shared Care Planning (SCP) Implementation Guide - Local Development build (v0.2.0) built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) Build Tools. See the Directory of published versions
Security - Authentication
Shared Care Planning (SCP) provides a way of distributed and planning of complex use cases in digital information exchange within healthcare. The cornerstone of all exchange is the authenticity of the actors that exchange information. In order to achieve the right level of authenticity the SCP relies on Trust over IP.
The primary entity being identified and authenticated is the legal organization providing care. For instance, a hospital, home care organization, or a pharmacy. The organizations should be identified by a unique identifier. Which identifier is used depends on local regulations, such as the URA number in the Netherlands. This unique identifier is then used as logical identifier to refer to the organization from the CarePlan, Tasks, CareTeam, and other resources if applicable. These unique identifiers should be issued by a trusted source, and authenticated in a cryptographically secure way according to TrustOverIP (ToIP).
Authentication through OAuth2
SCP uses OAuth2 to authorize access to its services. Care Plan Contributors and Care Plan Services act as OAuth2 Resource Servers, using an OAuth2 Authorization Server to identify and authenticate users. Clients are informed by the resource server using well-known Resource Server Metadata, a proposed RFC that allows resource servers to convey the information needed to interact with it.
Resource servers MAY use any of the specified metadata, but MUST use include at least the following fields:
resource: the FHIR base URL of the service (Care Plan Contributor or Care Plan Service).authorization_servers: JSON array containing URLs of allowed OAuth2 Authorization Servers, containing at least 1 entry.
The well-known location of the metadata is /.well-known/oauth-protected-resource, appended to the FHIR base URL of the service.
This is contrary to RFC8615, but follows the convention of other FHIR well-known metadata endpoints.
Trust over IP
The Trust over IP framework makes use of Trusted Sources or Trusted Third Parties that issue authentic properties to the participants. These parties are called issuers within the Trust over IP framework.
The participants, that get the 'authentic properties' from the issuers, are able to store these properties within a wallet-like solution as a verifiable credential (VC). These participants have the role of the credential holder.
The third and last role in ToIP is the verifier. A verifier can ask a holder to present a VC that may contain an (healthcare) organization-identifier. The holder will present a verifiable presentation (VP) to the verifier.
The role of verifier is to verify both the issuer and the holder that are part of this verifiable presentation. By doing this, the verifier can achieve the right level of authenticity required for the exchange of information required by SCP. In extension to that, Trust over IP delivers the following benefits:
- International and established standard, part of EBSI and the European wallet.
- Decentralized, there is no need for a central services (like an Identity Provider in OpenID Connect) while verifying a VC.
- Flexible, trust networks can be created whenever needed.
- Simple in its core, VCs and VPs are manifested as commonly used signed JSON objects (JWS).
Verifiable Credential to FHIR Organization
Given the organization authenticates itself using a Verifiable Credential, the attributes contained within can be used to create or derive the FHIR Organization resource. This identification mechanism is flexible: any type of Verifiable Credential (and even non-Verifiable Credentials) can be used, as long as parties agree on a trusted source (issuer) and presentation format.
Future Considerations
The implementation of Trust over IP requires trusted sources that provide assertions about both individual caregivers and organizations involved in healthcare. At the time of writing this specification, there are no official trusted sources available for both individuals and organizations. However, initiatives such as "IAA in de zorg" are trying to resolve this issue. This section outlines how authentication could be implemented in the future when the trusted sources for individual caregivers and care organizations are available.
Structure
The structure of the credentials that act as sources of trust are:
- The PractitionerRole credential, that contains:
- The Practitioner identifier
- The Organization identifier
- One or more roles, that the practitioner fulfills at the organization
- The Organization credential, that contains:
- The Organization identifier
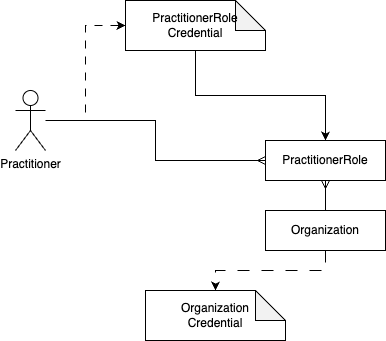
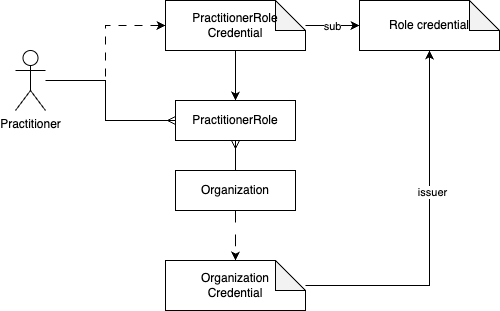
Alternatively, the role can be assigned by the organization itself. Thereby the organization becomes the trusted source itself. As the organization holds an Organization Credential the verifier is able to verify the authenticity of both the professional and organization, and the assigned role issued by the organization.
Practical implementation
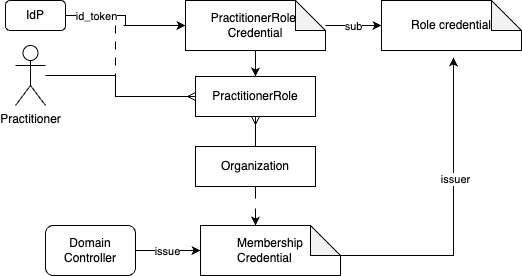
As the sources of trust are not available yet, we need to work with whatever is around right now. The tentative credential structure will be:
- The NutsEmployeeCredential, represents a login of an employee by wrapping the id_token.
- The membership credentials is assigned to an organization by an issuer with the role "domain controller".
- The Role credential is issued by the organization to the owner of the EmployeeCredential.